Reimagining Scientific Engagements During COVID-19
AUTHORS
Ka Weng Mah1, MSc; Ka-Wing Chong2, PhD; Kelly Lo3, BPharm; Victoria Elegant4, MBBS, DRCOG, FFPM
AUTHOR AFFILIATIONS
1Medical Capabilities Director, Japan and Asia Pacific Medical Affairs, Amgen
2Digital & Medical Education Lead, Japan and Asia Pacific Medical Affairs, Amgen
3Field Medical & Insights Lead, Japan and Asia Pacific Medical Affairs, Amgen
4Vice President & Head, Japan and Asia Pacific Medical Affairs, Amgen
This publication represents the consensus opinions of the authors and various members of MAPS, but does not represent formal endorsement of conclusions by their organizations.

INTRODUCTION
The COVID-19 pandemic has swept across the world, affecting every country with ongoing and recurring waves of infection. Countries in the Asia Pacific region were the first in the world to introduce lockdowns, masking and social distancing measures. There was massive reallocation of healthcare resources across all countries, forming a concerted effort to combat the pandemic. These responses reshaped the healthcare ecosystem and pharmaceutical industry, particularly in the engagements with healthcare professionals.
In light of the ongoing disruptions, it is essential that Medical Affairs teams examine and better understand the healthcare and Medical Affairs landscape during and eventually after COVID-19 in order to set a clear path forward. Project Phoenix, the brainchild of the Amgen Japan and Asia Pacific (JAPAC) Medical Affairs team, was initiated to address this need. This project comprises of four stages (Figure 1) that serves as a model for reimagining scientific engagement during and post-COVID-19.
This paper shares key findings with industry peers in order to i) advance the footprint of Medical Affairs in Asia in the peri-/post-COVID era, and ii) encourage and explore innovative new ways of working.

Figure 1. The four stages of Project Phoenix developed by the Amgen JAPAC Medical Affairs team.
COVID-19 IMPACT ON HEALTHCARE & PHARMA LANDSCAPE
The evaluation the external and internal landscape comprised of a literature review of ten key articles (listed under Bibliography), an external survey of healthcare professionals (HCPs, n=210, conducted between 11 May and 12 June 2020) and an internal survey of medical science liaisons (MSLs, n=53, conducted from 2 to 8 June 2020) in Asia Pacific. This section summarizes the key findings from the literature review and surveys.
Patient/family/caregiver ecosystem
The pre-COVID-19 patient care pathway has been significantly disrupted, especially for chronic diseases. Consultations, elective surgeries and procedures and laboratory testing have been postponed or cancelled whilst diagnosis and treatment have also been delayed.1-3 Concurrently, remote patient treatment and telemedicine have increased in use including funding from government to accelerate uptake.1-3 Pharma has the opportunity to support patients through building and implementing digital and remote tools to engage and educate patients as well as ensuring consistent drug supplies, accelerating access to treatments and increasing the affordability of treatment during the crisis and recovery period.2
Healthcare systems
HCP surveys indicate that approximately 70% of HCPs reported a decrease in face-to-face patient visits, causing a severe backlog and financial strain on practices. Concurrently, there has been a >1500% increase in the use of telehealth and digital tools to support patients, though there are payment and reimbursement challenges.1-3 Physicians were of the opinion that Pharma could provide additional support on disease education and telemedicine for patients during COVID-19.2 Moving forward, there is a need to identify new ways to support healthcare systems, improve and increase Pharma-patient support models and use innovative collaborations to drive care delivery and conduct telemedicine/telemonitoring education.2
Clinical trials
More than 50 pharmaceutical companies have halted new or ongoing non-COVID-19 trials,1 while 9 out of 15 of the top pharmaceutical companies have seen the majority of their sites reduce clinical trial activities.2 The main reasons for this are restricted site access and reduced availability of investigators and resources, whereby CROs are unable to send staff to monitor trials, and patients unable to access hospitals. As a result, Pharma needed to re-evaluate clinical trials operation and designs of protocols. For current trial operations, digital methods for site selection were initiated and remote monitoring was implemented. For upcoming trial designs, there is a need to identify and optimize opportunities for site and country selection based on geography, technology readiness, and plan for virtual / hybrid trials. Increased agility in evidence generation is required, utilizing innovative collaborations to decentralize trials, as well as to scale and accelerate virtual and digital clinical trials.1,2,4 In Australia, there is an initiative underway supported by government and other organisations to move towards teletrials. ,5
Product launch planning
Plans for the launch of an estimated 390 products in 2020 through to 2028 have been disrupted.1 Furthermore, gaining stakeholder traction and patient acquisition are rising concerns for recently launched products. Driven by recent and current launch underperformance, the industry could rack up an estimated cumulative loss of USD$10 billion by 2028.1 Digital solutions to accelerate launches are required, for example, through virtual thought leader and omnichannel engagement. Portfolio investments need to be re-prioritized based on revised market expectations and product differentiability. To our knowledge, there were two major product launches being carried out fully remotely during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Key learnings from these case studies will provide valuable information as companies seek to apply and improve for similar scientific campaigns in the future.
Pharma-HCP engagement
Pharma-physician engagement has seen a rapid transformation from face-to-face to digital interactions. However, there is a gap in virtual tools, and Pharma is working to build capability and infrastructure and prepare for long-term utilization of virtual channels. Based on our survey findings, regular scientific engagement is highly valued by our HCPs – 52% would like to interact monthly or more frequently, while 26% would like to interact every 3 months or less. The most preferred platforms to access Medical Education and Scientific Information among HCPs include live speaking webcasts, peer to peer discussions and on-demand web content. Results from the internal MSL survey showed that MSLs spend approximately 40% of their time on HCP engagement. The largest virtual competency gaps identified were the ability to conduct highly interactive virtual engagement sessions and to collect insights during virtual interactions.

COVID-19 IMPACT ON MEDICAL AFFAIRS
Based on these findings, these are the potential impacts of COVID-19 on Medical Affairs operations.
Patient/caregiver and HCP dynamics
COVID-19 has hastened changes in patient engagements and the hospital environment. The health care environment has quickly evolved, particularly in terms of interactions with patients and their caregivers. There is a marked increase in contactless care and virtual disease management (eg. telehealth).
Advanced data analytics capabilities
To deal with the widespread disruption to physical activity, pharmaceutical companies are being forced to step up data analytics capabilities to improve engagement. Big data and business analytics should be prioritized to inform omnichannel planning and engagement strategies, R&D and reimbursement. AI technology can also be used to augment HCP capacity. This could be done through establishing partnerships with external digital health start-ups, gaining a deeper understanding of digital health needs for each TA, incorporating digital into evidence generation and bridging digital health collaborations with HCPs through MSL engagements.
Hyper-focused scientific engagements
While it is inevitable that in-person engagement activities will resume, it is acknowledged that there will be an increase in the use and acceptance of digital interactions moving forward. There is an expectation amongst HCPs that Pharma would embark on holistic individualized scientific engagements using advanced digital platforms and content transformation . With these expected changes, there lies an opportunity to evolve and redefine the MSL role to further enrich scientific engagements with OLs. There also needs to be an expanded focus on patient education, HCP education initiatives, advisory boards and publications.
Clinical trial execution
Due to the widespread restrictions on movement and face to face interactions, it is apparent that there will be a noticeable shift in how clinical trials are conducted. Therefore, it is imperative that companies move into adaptive and collaborative trial designs and develop virtual trial capabilities, such as teletrials. There are plans to pilot these changes by incorporating virtual elements (e.g. e-consent, telemedicine) into future studies.
Organizational culture and infrastructure
With the shift to digital and new capabilities, change management on culture and infrastructure is central to support the evolution of the organization. A new medical affairs phenotype and enhanced skill set is needed to deal with compliance, new ways of interaction, and new compliance regulations.
There may be a need to review current processes to increase effectiveness and efficiencies, redefine new capabilities, examine cross-functional roles and outsource tasks which are necessary but not a strategic part of the core Medical Affairs functions. There is also a need to update regulation and compliance. Medical Affairs should also work on building systems and platforms to automate activities which can be automated (eg. content development and chatbots), to free up staff for more innovative initiatives, as well as upskill internal staff capabilities for clinical trials, evidence generation and digital.

LOOKING TO THE FUTURE
In view of the rapidly evolving patient/caregiver and HCP dynamics, these are the likely future realities in Medical Affairs:
- Patients (and their caregivers) in addition to HCPs, will be the core/center of Medical activities
- Successful Medical teams will use innovative, modern approaches in scientific engagements
- Leading Medical teams need to invest in and incorporate rapid and radical digital transformation to ways of working
- Medical Affairs leaders will need to continue to adapt to these changes and continue to evolve in an agile, strong andinnovative fashion
It is anticipated that these realities will guide the development of future strategies by medical teams. There should be an emphasis on virtual engagements with HCPs, educational offerings (particularly digitized content) and evidence generation. Other areas of focus include clinical trials, change management, talent management and upskilling, digital and outsourcing in order to improve productivity. A robust change management strategy is required, with prudent resource allocation to ensure building of new capabilities.
In line with these future realities, strategies and solutions were identified and distilled to the following core recommended actions (Figure 2) to ensure that Medical Affairs are in the best possible position to adapt and thrive within the evolving healthcare landscape.
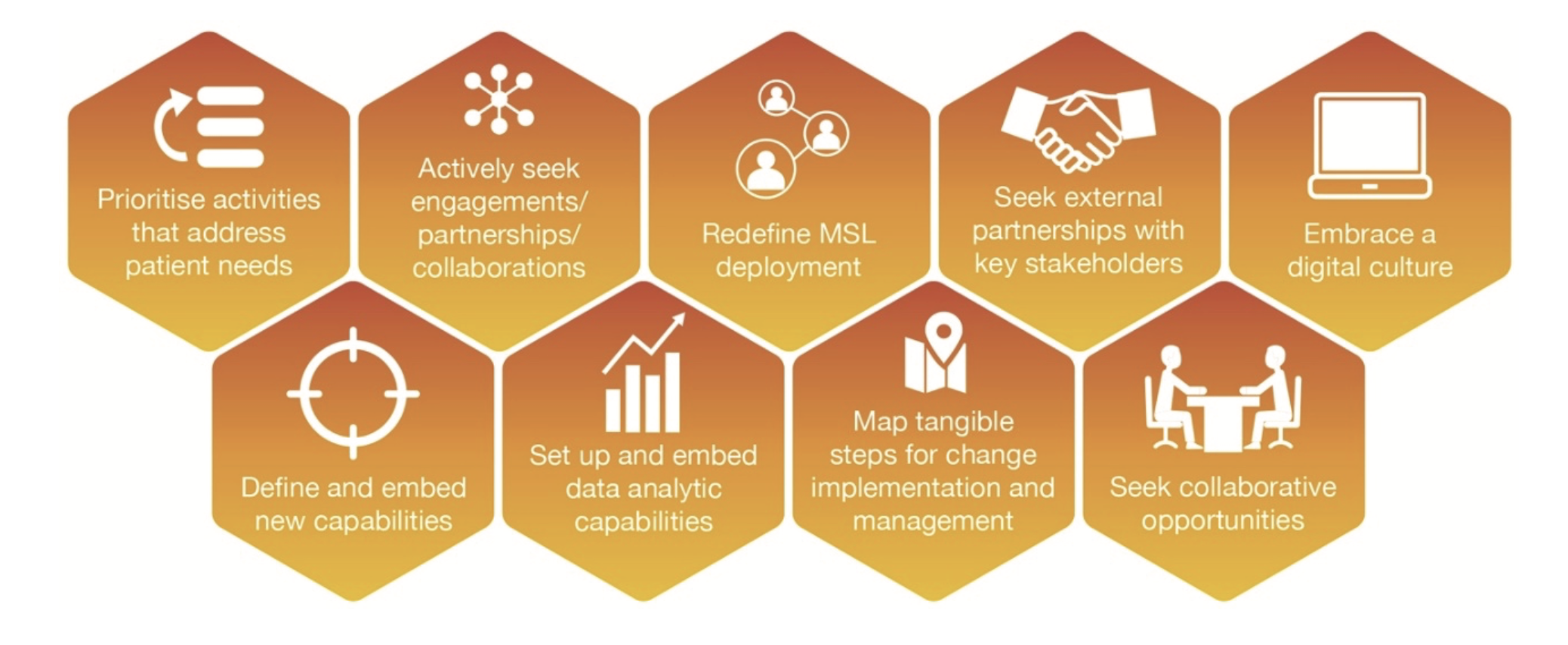
Figure 2. Core recommended actions for Medical Affairs teams.
CONCLUSION
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is evident throughout all industries including the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry. Medical Affairs activities were not spared, with disruptions to face-to-face activities and local/regional restrictions affecting every level of scientific engagement.
Amgen JAPAC Medical Affairs team’s Project Phoenix documents the “investigate, evaluate and formulate” steps that bridges the pre- to the peri-/post-COVID era for Medical Affairs teams, marking an essential milestone in the ongoing journey to improve patient outcomes and standards of care across the Asia Pacific region.

ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the Amgen JAPAC Project Phoenix working team (Simone Kaenzig, Riaz Abbas, Jaey Koo, Viola Wan, Motoki Sato, Sheetal Mistry, Rebecca Kannourakis) and Anish Sule (IQVIA) for their support and assistance in analysing the read outs & providing advice. We thank Dr Ee Lyn TAN for editorial support.
Our industry partners (IQVIA, Mckinsey & Company, Indigene) provided reports and insights which helped give us an understanding of the medical affairs environment in this region.
The voluntary participation of MSLs and HCPs in the surveys are greatly appreciated.
REFERENCES
- IQVIA, COVID-19 Global Executive Briefing, Driving Business Continuity April 20, 2020.
- McKinsey & Company, Medical Affairs in the time of COVID-19 – preparing for the next normal April 2020.
- Compass Inc CMI, What HCPs want and Need from Life Science Companies, During the COVID-19 Pandemic, April 10, 2020.
- Parexel. Part 2: Learnings from China: Managing in the time pandemic.
- Collins, I., Burbury, K. and Underhill, C., 2020. Teletrials: implementation of a new paradigm for clinical trials. MedicalJournal of Australia, 213(6), p.263.
BIBLIOGRAPHY (FOR LITERATURE REVIEW)
- Across Health. Reimagine Customer Engagement: COVID-19 and Beyond.
- Indegene. Driving Medical Affairs Towards a Digital Future. A Summary of Research Interviews.
- Indegene. Digital “Reset” for the New Normal.
- IQVIA: COVID-19 Global Executive Briefing, Driving Business Continuity April 20, 2020.
- James Kinross, a consultant surgeon at Imperial College Healthcare.
- McKinsey & Company: Clinical Operations Roundtable survey (April 2020).
- McKinsey & Company: Medical Affairs in the time of COVID-19 – preparing for the next normal April 2020.
- McKinsey & Company: A vision for Medical Affairs in 2025.
- Medical Affairs Professional Society (MAPS) 2020. ASIA PACIFIC Townhall meeting.
- Parexel: Part 2: Learnings from China: Managing in the time pandemic



