Connect with Us
602 Park Point Drive, Suite 225, Golden, CO 80401 – +1 303.495.2073
© 2025 Medical Affairs Professional Society (MAPS). All Rights Reserved Worldwide.
Evolution or revolution? Innovation in the Medical Affairs environment
Some of the fundamental responsibilities of Medical Affairs teams involve ingesting, interpreting, contextualizing and surfacing insights from complex life sciences innovations to actively support bringing them to market. At the same time, the way medical divisions work and the innovation-fostering ecosystem they operate in change constantly. This transformation is driven by a wide range of factors, including digital mechanisms, societal shifts, demographic changes, the impact of the pandemic and cultural considerations.
In this article, the authors discuss how to foster innovation within and across the Medical Affairs landscape, empower teams to deliver the best outcomes for patients and revolutionize healthcare delivery.

Matt Lewis, Global Chief Artificial and Augmented Intelligence Officer, Inizio Medical

David Woods, VP, Medical Analytics and Innovation Portfolio Lead, Inizio Medical
Defining ‘innovation’ in Medical Affairs
Innovation represents a novel solution, process, or system that effectively resolves a long-standing problem that has proven difficult to solve. A crucial aspect of innovation is its ability to scale and create a significant impact. It is essential to differentiate between finding a solution for a localized issue and true innovation. For instance, if an individual worker solved a problem on their personal desktop computer, it would not be categorized as innovation. For innovation to be truly successful, this problem-solving mindset must permeate throughout the group, department or business, ensuring widespread implementation. Therefore, for any solution to be recognized as ‘true’ innovation, it must have the potential to scale and persist over time.
In the context of Medical Affairs, innovation focuses on transforming the ways to comprehend, interpret and communicate scientific discovery and progress, and on engaging with stakeholders across the entire spectrum of scientific content communication and commercialization. It is not solely about generating data for innovative medical compounds, as that responsibility lies with research and development teams. Rather, it revolves around enhancing communication and engagement with decision-makers involved in prescribing, purchasing or adopting molecules.
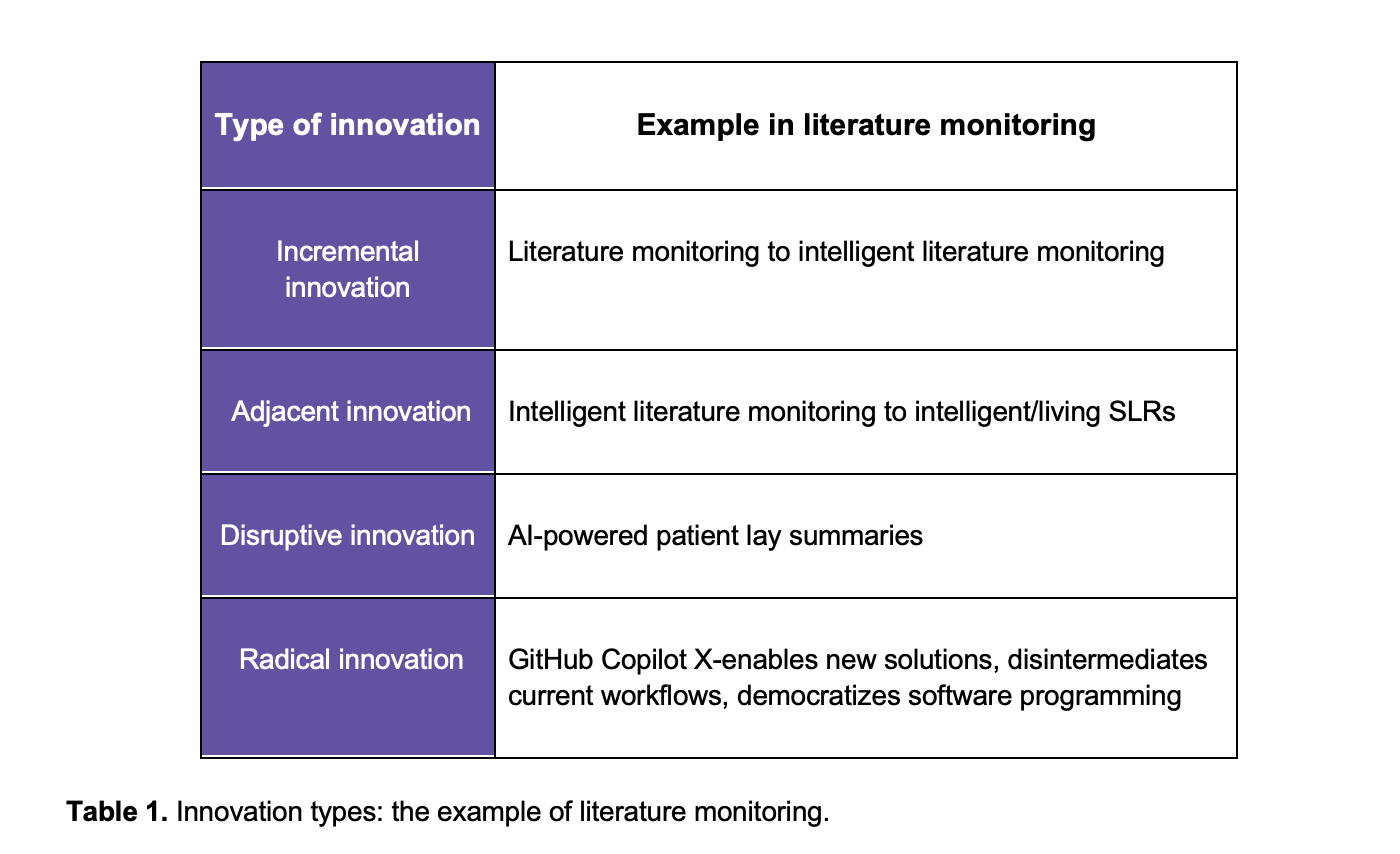
It is important to acknowledge that different types of innovation exist, ranging from incremental improvements to adjacent innovations and even more disruptive or radical changes. In Table 1, examples of key activities in Medical Affairs are provided, covering these four types of innovation.
Innovation – balancing burden/opportunity
A common observation is that in-house Medical Affairs teams frequently face a number of obstacles when it comes to driving innovation. Day-to-day, their core focus often lies in developing plans and executing tasks, such as conducting industry landscape analyses, often leaving scant time or remit for innovation.
One significant challenge the industry has faced over the past 10-15 years is the shift from a product-focused approach to a patient-centric one. The industry has been working to build its understanding and prioritize patients’ wants and needs when dealing with illnesses – augmenting the historical approach which focused solely on clinical outcomes. What makes this more challenging is that these wants and needs have been changing and they are bound to evolve further in the coming years. On the consumer side, people’s methods of accessing information and using essential services, such as banks and grocery stores, have changed significantly. In healthcare, digital transformation is progressing rapidly, leading to clinicians being primarily accessible through digital means.
The pandemic serves as a prominent case study, as it profoundly accelerated the need for change within Medical Affairs departments. The pharma industry continues to experience a shift toward a more nuanced, hybrid environment, where digital-first and in-person engagements have to be finely balanced. Some sectors are well attuned to these transformations but it has been a relatively novel challenge for Medical Affairs teams within pharma and biotech where more traditional, and proven approaches were relied upon as they were perceived to be the lowest risk option.
The impact of digital transformation and other macro trends on the life sciences field is extensive. Medical Affairs teams must embrace innovation to enhance communication with key stakeholders and effectively serve their patients. The pressure for innovation will remain, but the reactive approach to change seen during the pandemic must now be replaced by a future-gazing, outward-looking mentality that will better equip businesses to recognize change and adapt. This will be crucial to staying aligned with evolving patient expectations and industry advancements and will often require objective views and analyses from third parties to help unlock the creative thinking that allows Medical Affairs team to see and realize opportunities.
Introducing innovation frameworks
Once the space for innovation has been created and a growth mindset established, the next step is creating a mechanism to enable implementation. To successfully embed innovation throughout an organization, it is essential to establish an enterprise innovation framework. This framework serves as a strategic model that emphasizes the value chain from concept to customer, highlighting the common aspects shared by all enterprises. It strategically outlines areas for consideration when identifying innovation targets.
Once the innovation framework is in place, an innovation system should be established. This system can incorporate both formal and informal mechanisms to encourage internal and external stakeholders to participate in the innovation process. It should facilitate the surfacing of ideas and considerations, and provide mechanisms for scoring, validating, activating, resourcing, piloting, scaling and growing these ideas within the organization. Additionally, the system should ensure that feedback is provided to those who contribute their thoughts and insights.
By implementing a comprehensive innovation system within the organization, enterprises can efficiently foster a culture of innovation and provide a structured approach to support the development and implementation of innovative ideas throughout the entire value chain.
There are various approaches to sourcing innovative ideas within organizations. One option is for organizations to attempt to innovate internally, utilizing off-the-shelf software or internal resources. Alternatively, they can choose to collaborate with third-party innovation consultants. Many organizations have their own unique perspectives and comfort levels when it comes to risk-taking and exploring new ideas. In some cases, an external perspective becomes crucial for Medical Affairs teams to recognize the realm of possibilities and broaden their horizons.
Regardless of the approach taken, effective communication is vital when implementing any form of innovation. Communication should flow in all directions: upward to leadership, outward to experimental teams, downward to core business functions and ultimately reaching customers. It is essential for leadership to acknowledge that not all projects will succeed and proactively communicate this reality to their teams. They should provide reassurance that attempting innovation will not result in penalties or negative consequences. This creates an environment where the business can grow and learn, as failure is a natural part of the learning process and progress. Senior leaders should communicate openly and ensure their teams are aware that failure and learning are shared responsibilities and that they have the full support of leadership. Establishing a culture that accepts failure allows teams to take risks and communicate transparently with leadership.
By fostering open communication and a culture that embraces learning from failure, organizations can encourage their teams to take risks, explore innovative ideas and share their experiences openly with leadership. This approach facilitates continuous improvement and drives the organization forward.
Implementing innovation in Medical Affairs
The implementation of innovation in Medical Affairs involves four key stages:
It is widely recognized among senior life science executives that most pharmaceutical companies desire innovation. However, the life sciences are risk-averse by nature and companies typically prefer to observe successful implementations of innovation elsewhere before considering its adoption within their own environment. This cautious approach aligns with the necessary risk-averse mindset when dealing with patient lives. A mindset change is crucial for true innovation to thrive in this space.
Fortunately, there are ways to introduce innovation in a phased and controlled manner. This can be achieved through pilot programs focused on specific therapeutic areas, indications, geographies or teams. If successful, these pilots can then be scaled across other areas of the organization. This approach addresses concerns related to resource allocation, as the initial introduction of innovation is on a smaller scale.
Involving third-party innovation consultants can bring new perspectives and approaches to implementing an innovative mindset within a company. One example is open innovation, where startups and ecosystem players are invited to contribute their ideas and solutions, potentially leveraging AI technologies. This approach allows for a broader consideration of how the organization’s problems can be solved, without prescribing a specific method or approach. By presenting the problem and inviting diverse groups to propose solutions, multiple perspectives can be explored. With the necessary resources and support, Medical Affairs teams can experiment with potential solutions and, if successful, quickly scale them up across the business.
Utilizing artificial intelligence and omnichannel communication
A significant transformation that is increasingly impacting Medical Affairs is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is expected to be the most influential category of innovation in both professional and personal domains for the foreseeable future, with generative AI playing a prominent role. In the context of Medical Affairs, AI tools can be adapted to various tasks, such as generating content for delivery to physicians and patients. The methodologies of AI, including machine learning, deep learning and natural language processing, can be used to democratize data analysis, providing insights on how to effectively position medical products in the market. AI tools can process and analyze vast amounts of relevant content in minutes — a task that would have taken humans months or even years — thereby delivering vital data on white spaces and competitors. As a result, decision-making is accelerated, and with access to diverse data sources, more informed choices can be made.
When implementing innovation, Medical Affairs teams often look to other functional groups within the organization to develop their tactical approach. However, this may present challenges as some approaches work well in certain scenarios but not in others — with omnichannel communication serving as a good example. Before implementing an omnichannel approach to stakeholder communication, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and needs faced by stakeholders and to identify the most effective channels of communication. This is critical for creating differentiated customer experiences and customizing communication strategies accordingly. Senior leaders need to understand the problems that omnichannel communication can solve and optimize and tailor this approach as they plan for the future.
Adopting integrated innovation — leadership buy-in
Innovation can manifest within an organization in different ways, either integrated within the existing structure or as a separate innovation department responsible for driving new ideas. In most instances, the ideal approach is to integrate innovation and weave it into the fabric of the business as a shared responsibility among all teams. It means that everyone has an innovative mindset and sees implementing innovation as their responsibility. Innovation becomes a core element of how teams collaborate, promoting progress and growth throughout the organization.
To achieve this level of innovation implementation, it is crucial for the concept to be endorsed at the highest levels of the organization. The department head or chief medical officer must recognize the importance of innovation for success and understand that maintaining the status quo and continuing with the same activities will not lead to further achievements. Leaders need to adopt a different mindset, embracing the willingness to take risks, fail fast and experiment. Implementing cross-department multidisciplinary teams — supported by senior leadership — that bring together diverse functional groups within the organization to solve major problems is an effective way of driving innovation.
This approach must be accompanied with an allocated budget, appropriate resources and sufficient training for the teams involved. Strategic enablement and flexibility to experiment and implement pilot programs are necessary. If successful, these pilots can be scaled up and swiftly implemented across other functional departments. It is important to acknowledge that failures are part of the innovation process. Having the support of senior leadership who possess the vision and understanding of the future becomes crucial in providing the necessary backing for these initiatives, whether they succeed or fail.
Conclusion
The ever-evolving landscape of Medical Affairs necessitates a proactive approach to innovation. Medical Affairs teams play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between complex life sciences innovations and market implementation, with a focus on enhancing communication and engagement with stakeholders. Innovation within this context encompasses a spectrum, from incremental improvements to radical changes, all aimed at improving patient outcomes and aligning with shifting industry dynamics.
The potential for innovation in Medical Affairs teams is significant and the need for it has never been greater. Organizations must be willing to take operational risks and embrace ways of working that may be completely different from what has been done before. This willingness to challenge the status quo and pursue novel approaches is at the heart of true innovation which similarly requires space, time, resources and ownership for any ambitions to come into fruition.
Ultimately, integrated innovation, woven into the fabric of the organization, requires leadership buy-in, allocation of resources, and a willingness to experiment and take risks. While the life sciences industry is inherently risk-averse, phased approaches and collaboration with third-party consultants can facilitate innovation adoption. This are instrumental in driving innovation initiatives forward, ensuring that they succeed in adapting to the dynamic medical landscape. Embracing innovation is not just a choice but a necessity for Medical Affairs teams to thrive in the future of healthcare delivery.
602 Park Point Drive, Suite 225, Golden, CO 80401 – +1 303.495.2073
© 2025 Medical Affairs Professional Society (MAPS). All Rights Reserved Worldwide.

 Introducing an Omnichannel Approach in Medical Affairs
Introducing an Omnichannel Approach in Medical Affairs